Pull requests allow developers to collaborate with each other on a code change before
merging it into another branch on a GIT repository.
Pull request is a fully integrated solution of the code browser component. It
supports all the basic functionality such as creating, viewing, updating,
abandoning, rebasing and merging of pull requests. Using a pull request, you notify
others about a feature or fix change that needs attention.
Important: You can access the pull request feature only when the repository
owner enables the feature and sets the code review policy on the tab.
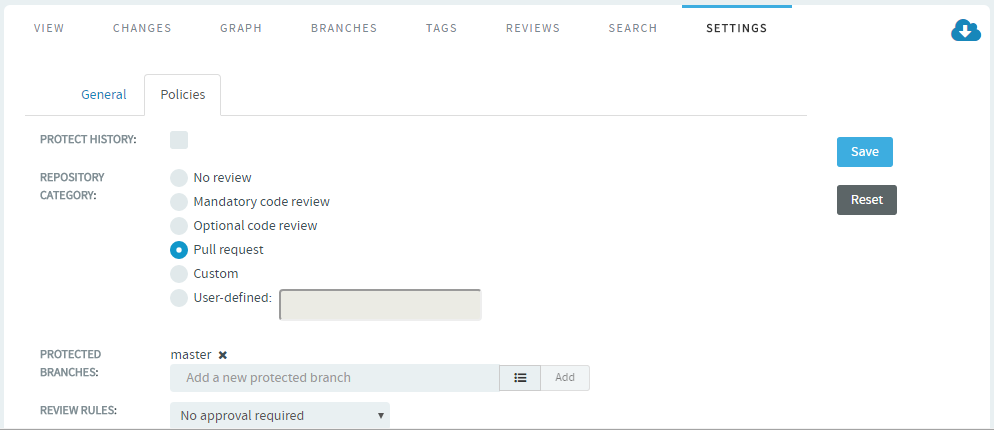
Configure "Pull Request" for repositories
In order to use pull requests in your Git repository, you need to set up proper
permissions in your repository so that your policies are being followed.
Configure the repository from the Settings tab.
-
Click SOURCE CODE from the Project
Home menu.
-
Browse and open the Git repository in the code browser.
-
Select .
-
Select Pull request for Repository
Category.
The Protected Branches and Review
Rules fields show up. For more information about Repository
Category, Protected Branches and Review Rules, see Review code.
|
|
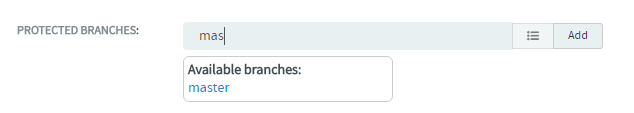
| Add one or more protected branches. Type the branch name,
select the branch and click
Add. |
|
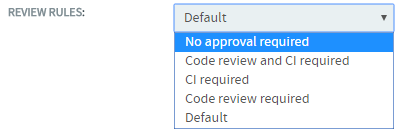
| Select one of the review rules from the drop-down
list. |
|
-
Click Save.
Create a pull request
When you are ready to merge the change, or at least to start getting feedback,
you should create a pull request. You can do this easily from the
Branches tab by clicking on the
Create button for your feature branch.
-
Go to the Branches tab on a Git repository page.
-
Click Create.
-
Select the source branch which is wanted to be merged.
-
Select the target branch to which you want the changes to be merged.
-
Give an appropriate subject line and description that will be used as a commit
message for a merged pull request.
Optionally you can provide a summary of the pull request. This supports
markdown formatting.
The Commits tab at the bottom of the page displays the
list of commits made in the selected source branch. The
Files tab shows the difference between the source
and target branch.
-
Click Create Pull Request.
-
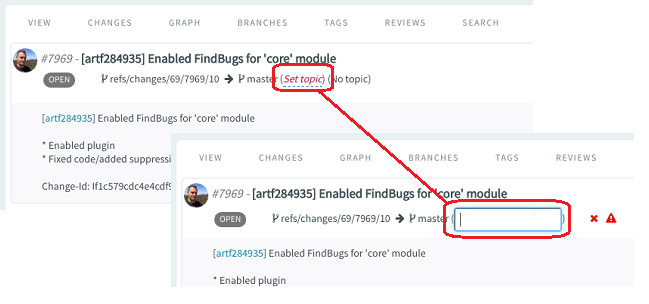
Submit whole topic: You can now bundle related changes (code reviews) by
topic and submit the whole topic for review instead of just submitting changes
one-by-one. Just open a review, click the Set Topic link
and enter the topic name.
-
As a reviewer, click the pull request that you want to review from the list of
open pull requests on the Reviews tab.
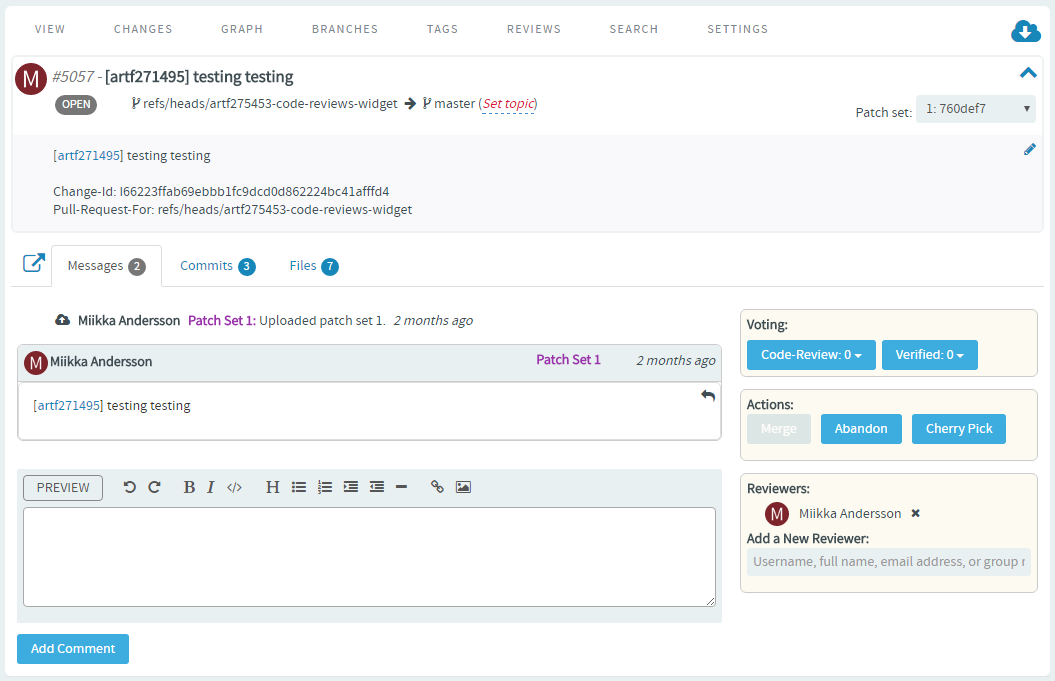
Review a pull request
In addition to the
requested reviewers, anyone with access to the repository and who wishes to
comment on the pull request can review and post their comments on the pull
request details page.
-
On the pull request details page, you can switch between three views:
Messages, Commits and
Files. Click the Commits tab to
view the list of commits. Click the Files tab to review
the code changes made in each file. You have the option to view the difference
between the source and target branches.
-
Once you have reviewed the changes, on the Messages tab,
enter your comments and give an appropriate voting as well.
Note: The message section supports markdown formatting with a preview
option.
-
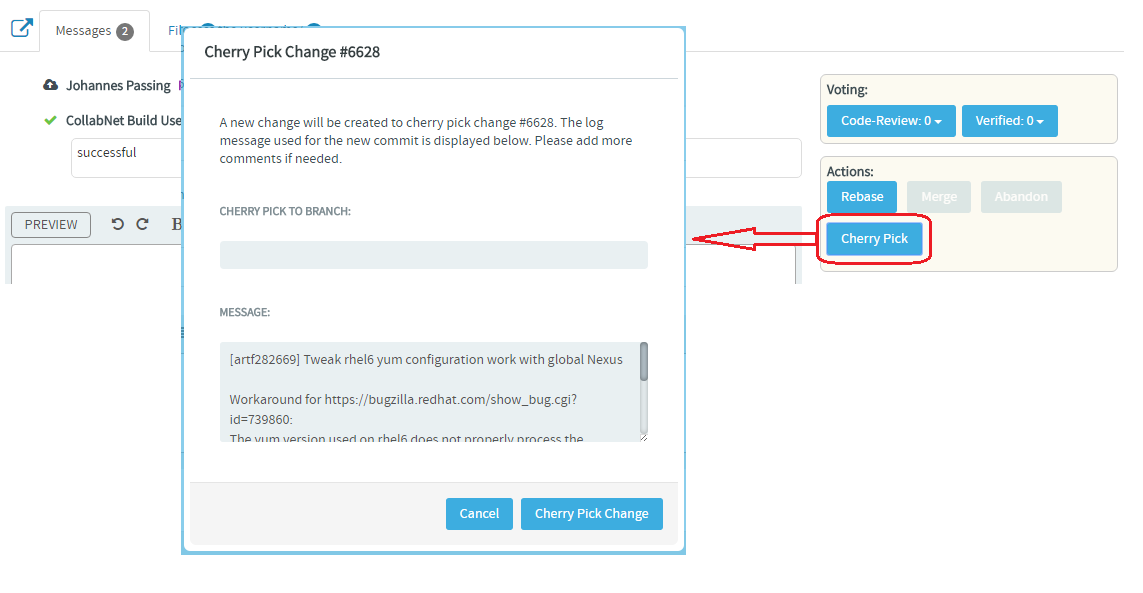
Cherry Pick: Apply the changes introduced by existing commits: You can
also cherry pick and apply changes introduced by existing commits to another
branch. For example, you can now use this Cherry Pick function in TeamForge's
native code browser to apply a commit in master to a release branch.
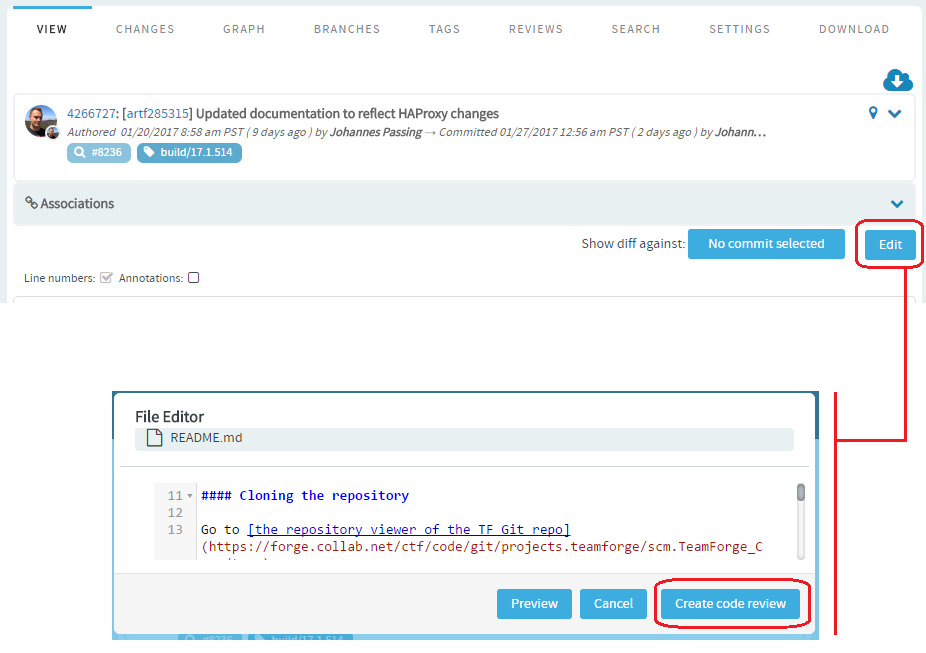
Inline editing of files
-
Quick changes to files, if required only to few files, can be done using the
inline edit feature from within the code browser without having to clone an
entire repository. Browse the repository, locate and open the file in the
View tab, click Edit to open the
file in the File Editor, make your changes,
Create code review and Publish
your changes for review.
-
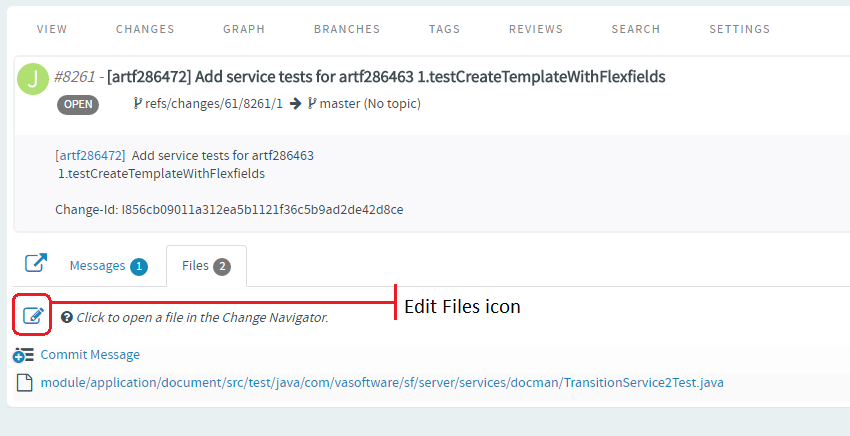
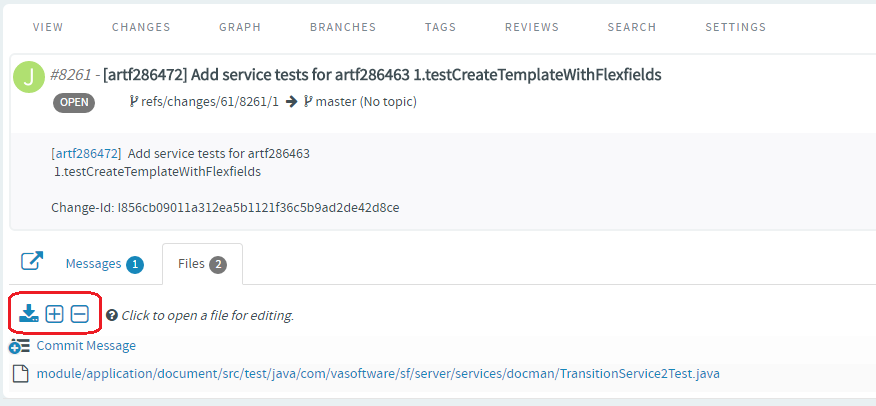
You can also add new files to a review and delete files from a review by
clicking the Edit Files icon and then the "+" and "-"
icons respectively.
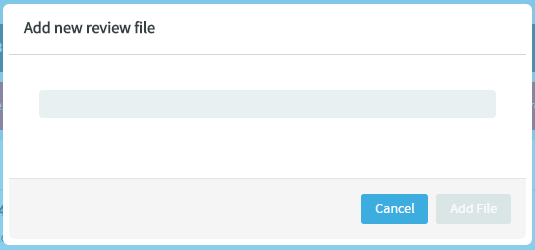
Type the name of the file to see results matching the file name, select a
file and click
Add File.
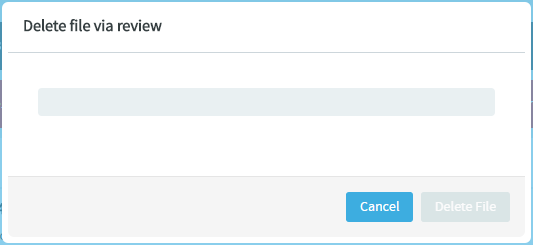
Type the name of the file you want to delete to see results matching the file
name, select the file and click
Delete File.
-
Click the Complete File Edits icon.
Merge (close) a pull request
Once the pull
request is reviewed, it is ready to be merged, that is the
Merge button on the pull request details page is
enabled only if the pull request satisfies all the repository specific
qualification criteria. For example, it is possible to merge pull requests even
without any voting if “no voting” has been defined as gating criteria. Also, it
might require both voting AND acceptance by Continuous Integration; basically it
totally depends on the gating criteria of the repository in question.
Note: These criteria are set by the repository owner in tab for the Pull Request Repository
Category.
-
Click the Merge button to merge the source branch into
the target branch.
- If the source branch is not updated with the latest changes, a merge
conflict is detected prompting you to rebase your request.
- Click the Rebase button. Once rebased, the pull
request has to be revalidated after which you can merge the pull request
into the target branch.
-
The newly-merged pull request is added to the list of merged pull
requests.
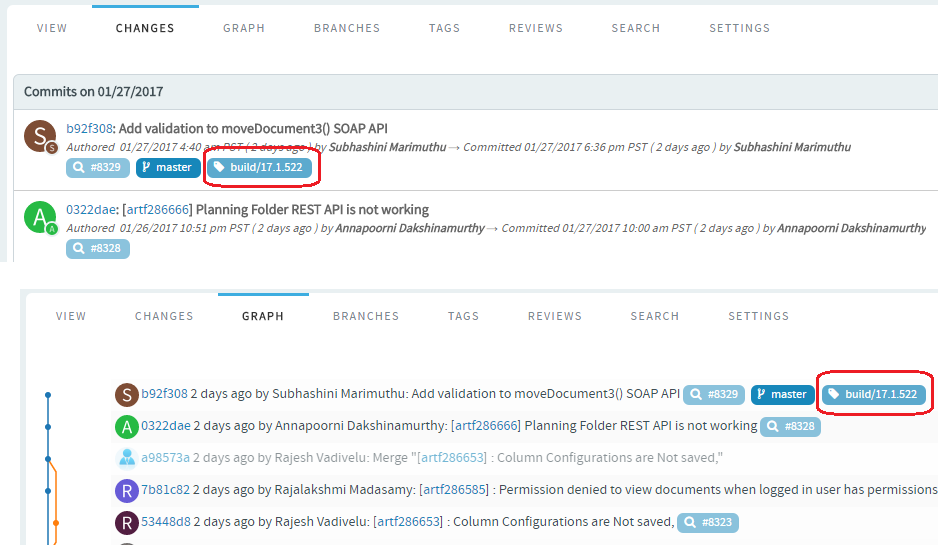
Note: Once merged, on the Graph view, you can see that
the merged branch has been added to the graph. A link to the pull request is
also provided.
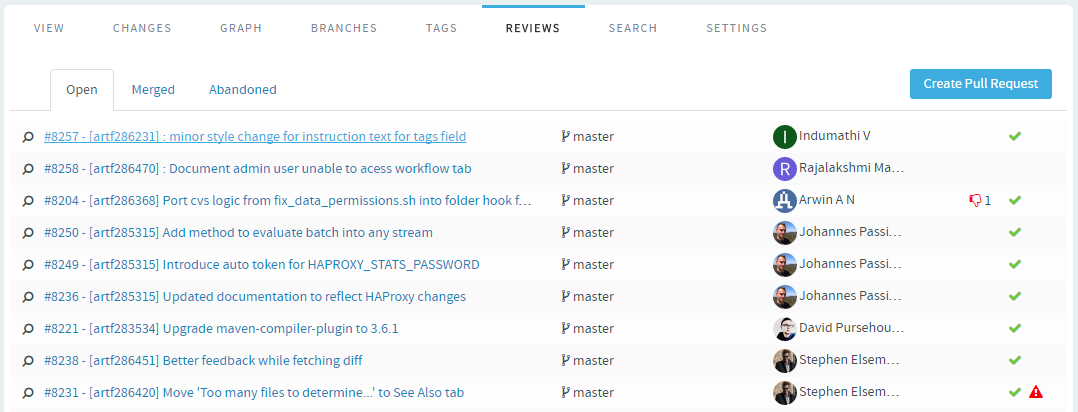
View pull requests
-
Click the Reviews tab on a GIT repository page. The pull
request details page displays the list of Open,
Merged and Abandoned pull requests
under appropriate tabs.
- For each pull request, the author, title, number of thumbs up/down, and
the time elapsed since the pull request was created, are shown.
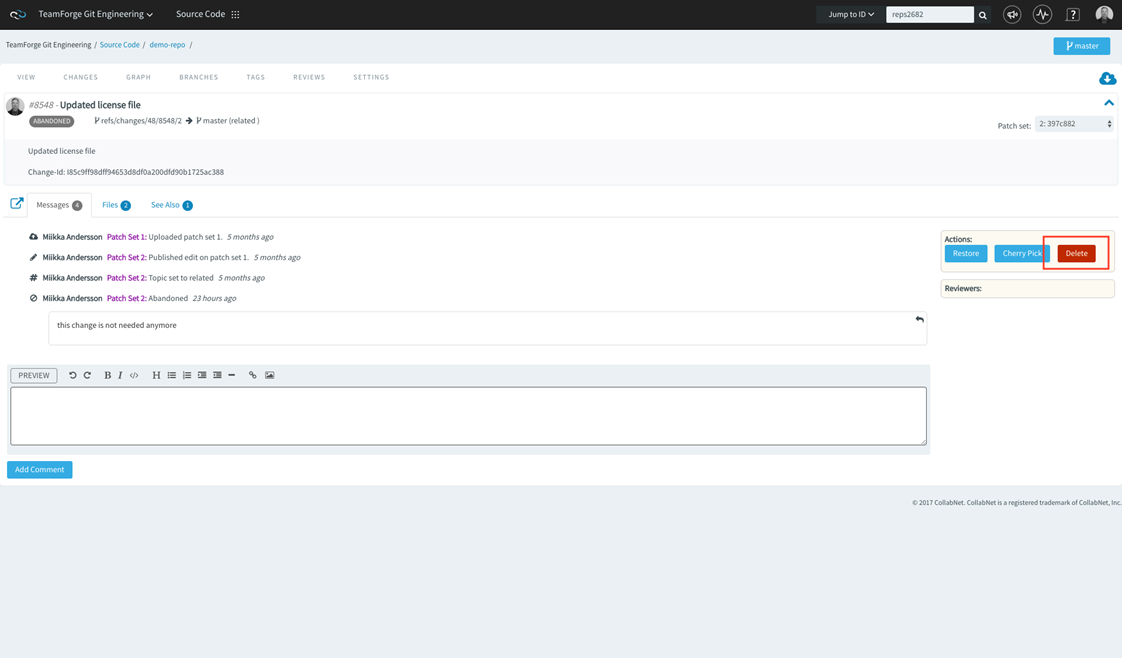
- On the Abandoned pull request details page, you
have the option to
restore
or delete an abandoned pull
request.
To restore or delete an abandoned review, open the review in the code
browser and click Restore or
Delete respectively from
Actions.
Tagging
-
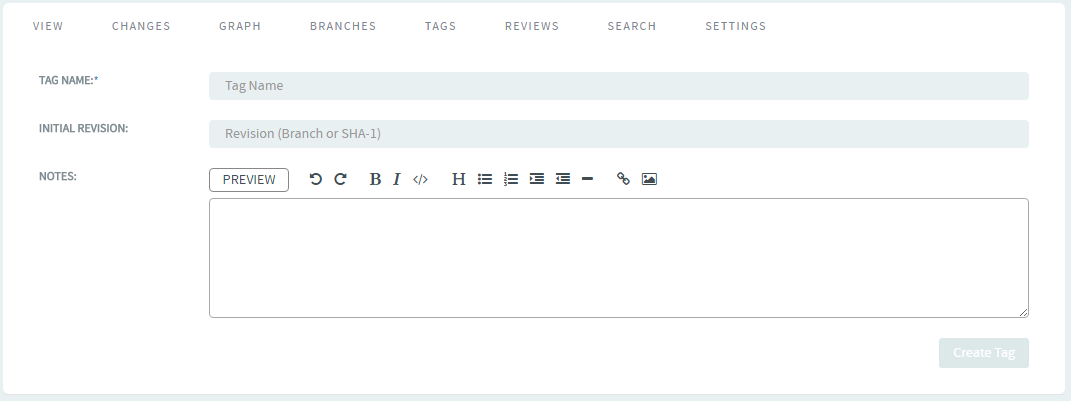
To create Git tags and tag specific points in history as being important (to
mark release points, for example, v1.0, and so on), select the
TAGS tab and click Create
Tag.
-
Type a tag name and revision number and add a Release Notes for the tag. Click
Create Tag.
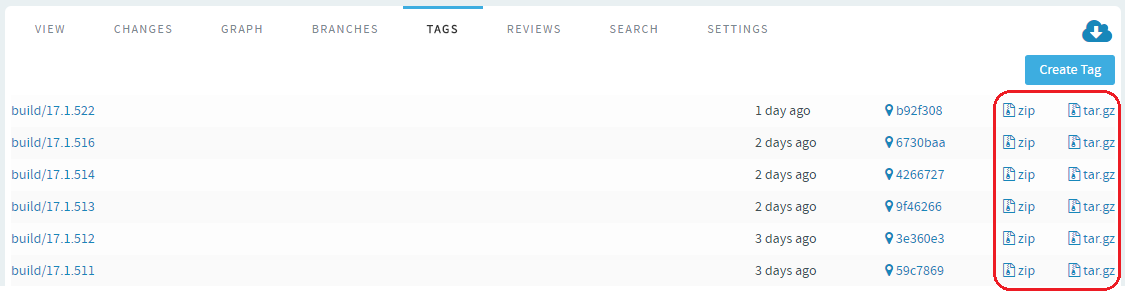
Once you create a tag, you can use it to donwload source code as a zip/tar
file and view the tag information in Changes and
Graph tabs.